Laser Welding VS Traditional TIG Welding
2025-05-26In the rapid development of the manufacturing industry, welding technology has always played an indispensable role in the core process of material connection. Laser welding and traditional TIG (abbreviated from tungsten inert gas welding) welding are two representative technologies, representing the typical paths of high-energy beam welding and arc welding respectively. Hereof, we will introduce the differences, advantages and disadvantages between laser welding and traditional TIG welding from the dimensions of working principle, processing efficiency, welding quality and application scenarios. This post, laser welding VS traditional TIG welding, may provide a reference to you for technology selection.
What is Laser Welding?
Laser welding is an advanced welding technology that uses a high-energy-density laser beam as a heat source to melt materials locally and form a strong connection through precise control. The core of laser welding is to generate extremely high energy density (usually up to 106~108w/cm2) by focusing the laser beam to achieve rapid melting and solidification, thereby completing high-quality welds.

What is TIG Welding?
TIG welding, the full name of which is Tungsten Inert Gas Welding, also known as GTAW (Gas Tungsten Arc Welding), is a welding process that uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode. This welding method uses an arc to generate heat between the tungsten electrode and the workpiece to melt the workpiece metal, while using an inert gas (usually argon or helium) as a shielding gas to prevent the welding area from being oxidized by oxygen, nitrogen, etc. in the air.
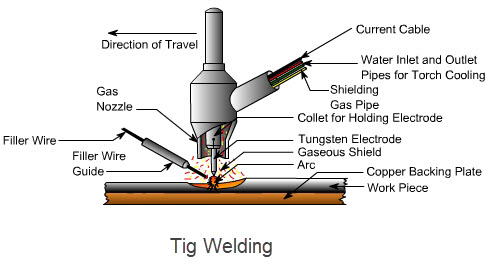
I. Laser Welding VS TIG Welding in Energy Source
The core of laser welding is to use high-energy laser beams (such as fiber lasers and CO₂ lasers) as heat sources, which are focused by optical systems to form a light spot with extremely high energy density (up to 106~108W/cm²), so that the material can be melted and welded in a very short time. Its non-contact working mode makes the welding process without mechanical pressure, which is suitable for high-precision scenes.
TIG welding relies on the arc heat generated between the tungsten electrode and the workpiece (energy density is about 104W/cm²), and protects the molten pool with inert gases (such as argon and helium) to prevent oxidation. Its contact process requires the operator to control the arc manually or mechanically, and has high requirements for welding stability.
Key difference: the energy transfer of laser welding is more concentrated and efficient, while TIG welding relies on the "surface heating" characteristics of the arc, and the heat input range is wider but dispersed.
II. Laser Welding VS TIG Welding in Efficiency and Speed in the Automation Era
The significant advantages of laser welding are high speed and high productivity. For example, in the field of automobile body welding, the laser welding speed can reach 5-10 meters per minute, and a single welding pass can penetrate a steel plate of more than 10mm, greatly reducing the need for multiple processes. This feature makes it the first choice for large-scale automated production, especially in the fields of new energy vehicle battery modules and consumer electronics precision structural parts.
TIG welding has a low arc energy density, and its welding speed is usually only 0.1-0.5 meters per minute, and thick plate welding requires multiple fillings of welding materials, which takes a long time. However, it is highly flexible, and manual operation is suitable for small batches and customized scenarios, such as repairing aerospace parts or fine welding of artworks.
Laser welding is suitable for high efficiency production which plays a core role in the automated welding process. TIG welding is better at polishing quality.
III. Laser Welding VS Traditional TIG Welding in Heat Input Control
Laser welding is particularly suitable for welding thin plates (less than 0.1mm) or precision components (such as sensors and medical devices) because of its small heat input, concentrated energy, extremely narrow heat-affected zone (HAZ), and low deformation rate of workpieces. In addition, its weld depth-to-width ratio is high (up to 10:1), the appearance is smooth, and no subsequent grinding is required. However, highly reflective materials (such as copper and aluminum) need to adjust the laser wavelength (such as green or blue laser) to improve the absorption rate.
TIG welding has a high heat input and a wide heat-affected zone, which may cause deformation of the workpiece (need to be controlled by fixtures or process optimization). However, its arc stability is strong and the weld surface is smooth, which is suitable for scenes with strict appearance requirements (such as welding of food-grade stainless steel containers). At the same time, TIG has more advantages in welding dissimilar metals (such as copper-steel, aluminum-titanium), and reliable connection can be achieved by selecting suitable welding wires.
The laser welding wins in stability and precision, while TIG welding wins in wide and flexibility.
IV. The Comparison Between Laser Welding and TIG Welding in Cost
The equipment cost of laser welding is high. A high-power fiber laser system can cost up to hundreds of thousands of dollars, and it needs supporting automation equipment (such as robots and CNC platforms). In addition, the maintenance cost of optical components (lenses, optical fibers) is high. However, its single-piece processing cost is low, which is suitable for large-scale production.
TIG welding equipment is simple, entry-level welding machines only cost a few thousand yuan, and consumables (tungsten electrodes, shielding gases) are cheap, which is suitable for small and medium-sized enterprises and maintenance scenarios. However, its labor cost is high and depends on the operator's experience (such as arc stability control and wire feeding rhythm).
V. Laser Welding VS TIG Welding in the Application Fields
Laser welding and TIG (tungsten inert gas shielded welding) welding have obvious differences in application fields, which mainly depends on their respective technical characteristics, advantages and limitations. The following is a comparison of the two in terms of application areas:
The applications of laser welding:
• Precision parts welding in the electronics industry, such as microelectronic packaging, circuit board welding…
• Welding of lightweight alloys, titanium alloys and other materials in the aerospace industry.
• Parts of the automotive industry that require efficient and high-quality connections such as body parts and battery packs.
• Welding of stainless steel and other biocompatible materials in medical device manufacturing.
The applications of TIG welding:
• In pipeline engineering and pressure vessel manufacturing, especially where corrosion resistance is required.
• Welding work in the nuclear industry where safety is extremely important.
• In artwork and sculpture production, because TIG welding can provide an aesthetically pleasing appearance.
• In food processing equipment manufacturing, because it can provide smooth and flawless welds, helping to maintain hygiene standards.
Generally, laser welding is more inclined to efficient and high-precision production environments, while TIG welding is more suitable for welding operations that require high quality and good repeatability.
VI. Laser Welding VS TIG Welding in Future Trends
With the advancement of technology, the composite welding technology of laser and TIG (such as laser-TIG Hybrid) has gradually emerged. Combining the high penetration of laser and the bridging ability of TIG can solve the limitations of a single process. For example, in aluminum alloy welding, the laser is responsible for deep melting welding, and the TIG arc supplements heat and improves surface forming, significantly improving the welding quality.
Conclusion
• It is better to choose laser welding when you pursue high efficiency, automation, high precision, and large-scale production with sufficient budget.
• It is better to choose TIG welding when you need flexible operation, welding of dissimilar materials or small batch customization.
The two are not substitutes, but complementary coexistence. In the future, with the advancement of intelligent manufacturing and materials science, welding technology will continue to iterate. After reading this post upon laser welding VS traditional TIG welding, have you got any opinion about it? Any questions or thoughts about welding techniques or our laser welding machines, please drop us a line.