Ceramic Materials Laser Marking
2025-12-16In modern industrial systems, ceramic materials, with their excellent physical stability and chemical inertness, have been deeply integrated into numerous applications, from high-precision electronic devices to heavy equipment operating under extreme conditions. As a durable, aesthetically pleasing, and widely applicable key material, ceramics require efficient and precise surface marking. However, achieving clear and durable markings on such hard and chemically stable surfaces has long been a challenge for the manufacturing industry. With continuous breakthroughs in laser processing technology, advanced ceramic laser marking processes have emerged, providing a new and green solution for industrial marking. Here, we will explore which ceramic surfaces can be marked with lasers, the challenges and considerations, and recommend suitable equipment. If you are looking for ceramic laser marking solutions or machines, please take a moment to read the following content. We hope it will be helpful.
I. Can Laser Mark Ceramic Materials?
Yes, ceramics can absolutely be laser-marked. In fact, in modern industry, laser marking has become one of the mainstream technologies for the identification, traceability, and decoration of ceramic materials. Laser marking on ceramics essentially involves a high-energy laser beam interacting with the surface of the ceramic material in a controlled physical or chemical manner. This creates a visible, permanent visual contrast area (such as black, white, or recesses) without damaging the overall structure.
Our engineers conducted a practical test using a NITRATEK UV laser marking machine to mark white Chinese characters on the surface of ceramic cups. The entire process was highly efficient and smooth—no ink or molds were required; in just a few seconds, a set of clear, delicate, and high-contrast white Chinese characters were stably "marked" on the ceramic surface. This effect not only meets the dual requirements of aesthetics and tactile feel for everyday ceramics but also provides a highly promising marking solution for high-end customized gifts, brand co-branded products, and cultural and creative products.
II. Why is Laser Marking Suitable for Ceramics?
Ceramics are ideally suited for laser marking primarily due to the high compatibility between their material properties and laser processing technology. Although ceramics are inherently hard, chemically inert, and heat-resistant, traditional marking methods (such as inkjet printing, screen printing, and mechanical engraving) often struggle to achieve clear, durable, and precise markings. Laser technology, however, can effectively leverage these strengths and overcome these weaknesses. The inherent properties of laser marking technology are highly compatible with those of ceramic materials, showcasing a natural technological advantage. Let's look at the specific reasons:
▄ High Hardness and Wear Resistance: Although ceramics are inherently hard and wear-resistant, lasers can create a permanent physical or chemical modification layer on the surface through high energy density, resulting in markings that are long-lasting and far superior to traditional printing or mechanical etching.
▄ Strong Chemical Stability: The excellent chemical stability of ceramics means that there is no need to use inks, solvents, or corrosive chemicals, avoiding potential chemical reactions and achieving truly environmentally friendly, reliable, and pollution-free marking.
▄ High Temperature Resistance: Although ceramics are inherently heat-resistant, laser marking only involves instantaneous heating in a micro-area, resulting in minimal heat impact and preventing damage to the overall thermal stability and structural integrity of the material.
▄ Dense and Smooth Surface: The dense and smooth surface of ceramics provides ideal conditions for laser focusing. Combined with micron-level spot precision, it can clearly render fine text, complex logos, or high-density QR codes.
▄ Good Insulation: Thanks to the excellent electrical insulation properties of ceramics, laser marking, a non-contact, current-free processing method, is particularly suitable for electronic ceramic components (such as substrates, sensors, and capacitors), ensuring a safe and stable processing process without affecting device performance.
For these reasons, ceramics are not only suitable for laser marking, but also one of the ideal materials for laser precision machining. The combination of their high stability and the high controllability of lasers enables permanent, clear, environmentally friendly, and intelligent marking solutions, making them an indispensable key process in modern advanced manufacturing.

III. What Are the Core Advantages of Laser Marking on Ceramic Materials?
The widespread adoption of laser marking on ceramic materials stems from the high degree of compatibility between its technical characteristics and the specific needs of ceramic materials. Compared to other traditional marking methods, such as screen printing, inkjet printing, and mechanical engraving, laser marking exhibits unique advantages on ceramics:
▄ Permanence and High Durability: Laser marking alters the physical structure (e.g., lattice defects, micro-melting) or chemical state (e.g., oxygen vacancy generation) of the ceramic surface, forming a mark integrated with the substrate. These marks do not peel off or fade and can withstand high temperatures, strong acid and alkali corrosion, mechanical friction, and cleaning and disinfection. Therefore, it is particularly suitable for fields with extremely high requirements for marking reliability, such as medical devices, aerospace, and electronic components.
▄ Non-contact and No mechanical stress: When marking ceramic items with a laser, no cutting tools or physical contact are required, avoiding micro-cracks or chipping in brittle ceramics (such as zirconium oxide and silicon nitride). Therefore, lasers are especially suitable for the safety marking of thin-walled, miniature, or precision ceramic components (such as sensor chips and dental implants).
▄ Ultra-high precision and detail: The laser spot can be focused to 10–30 micrometers, supporting extremely small characters, high-density QR codes (Data Matrix, QR Code), complex vector graphics, and gradient effects. This meets the precision marking needs of micro- and nano-manufacturing scenarios such as electronic ceramics, semiconductor packaging, and biochips.
▄ Clean and environmentally friendly, with no consumable pollution: When laser marking ceramic materials, the entire process requires no ink, solvents, masks, or chemical etchants, resulting in zero VOC emissions and no waste liquid generation. It complies with environmental and medical safety standards such as RoHS, REACH, and FDA, making it particularly suitable for cleanroom environments (such as semiconductor factories and medical device workshops).
▄ Flexible process and high degree of digitalization: During ceramic laser marking, the marking content is controlled by software, allowing for real-time changes to text, serial numbers, barcodes, and other information. It supports one item, one code, dynamic database linkage, and anti-counterfeiting encryption, making it easy to integrate into automated production lines and industrial systems for full-process traceability and intelligent management.
▄ High efficiency and energy saving, low operating costs. When laser marking ceramics, the single marking time is typically 0.1–3 seconds, resulting in fast marking speed. Furthermore, the laser has a long lifespan (fiber lasers can reach over 100,000 hours); there are no consumable replacements or mold making required, making long-term operating costs far lower than traditional processes.
Laser marking not only solves the industry pain point of difficult marking on ceramics, but also, with its comprehensive advantages of permanence, precision, environmental friendliness, and intelligence, has become the preferred technology for ceramic marking in high-end manufacturing. With the integration of technologies such as ultrafast lasers and intelligent visual positioning, its application depth and breadth in the ceramic field will continue to expand.
IV. Which Ceramics Can Be Laser Marked?
Laser technology can be used to mark the surfaces of various types of ceramic materials. The specific applicability depends on the ceramic's composition, structure, and the type of laser used, such as fiber lasers, ultraviolet lasers, and CO₂ lasers.
1. Oxide Ceramics
For laser marking of oxide ceramics (such as alumina Al₂O₃ and zirconium oxide ZrO₂), fiber lasers or ultraviolet lasers are generally recommended. Fiber lasers (wavelength 1064 nm, power 10–50 W) are suitable for efficiently achieving high-contrast "black marking" effects, especially suitable for industrial scenarios with speed and production capacity requirements; while ultraviolet lasers (wavelength 355 nm, power 3–10 W), with their short wavelength and "cold processing" characteristics, can achieve fine, clear white or light-colored markings without thermal damage, making them particularly suitable for applications with stringent requirements for precision and surface integrity.
2. Nitride Ceramics
Laser marking of nitride ceramics (such as silicon nitride Si₃N₄ and aluminum nitride AlN) typically employs fiber lasers (1064 nm, power 20–60 W) or ultraviolet lasers (355 nm, power 5–15 W), often operating in nanosecond pulse or high-frequency modulation modes. On these materials, laser action usually produces high-contrast markings ranging from dark gray to black, making them particularly suitable for industrial traceability and electronic component identification. However, while aluminum nitride (AlN) possesses excellent thermal conductivity, its anisotropic coefficient of thermal expansion makes it prone to thermal cracking at high energy densities. Therefore, a process strategy of lower power, higher frequency, and slower scanning speed is recommended to control heat input and avoid damage. Silicon nitride, on the other hand, is relatively more resistant to thermal shock and can withstand slightly higher laser energies.
3. Carbide Ceramics
Carbide ceramics (such as silicon carbide SiC and boron carbide B₄C) place high demands on marking processes due to their extremely high hardness, chemical inertness, and low laser absorption. Ultraviolet lasers (355 nm, power 8–20 W) or picosecond lasers (355 nm or 532 nm green light, power 10–30 W) are recommended, utilizing short wavelengths and high peak power to achieve micro-ablation or controllable light-colored marking. Excessively high single-pulse energy should be avoided to prevent material sputtering or micro-cracks. Therefore, the core of laser marking on carbide ceramics lies in the combination of short wavelength, high peak power, and precise energy control.
4. Piezoelectric and Functional Ceramics
Piezoelectric and functional ceramics (such as lead zirconate titanate PZT and barium titanate BaTiO₃) are extremely sensitive to heat. Their electrical properties (especially polarization) are easily degraded or even fail due to high temperatures. Therefore, laser marking must strictly control heat input. Ultraviolet lasers (355 nm, power 2–8 W) are the preferred solution. With their short wavelength, high photon energy, and "cold working" characteristics, they can achieve light-colored discoloration or micro-engraving markings on the material surface without causing significant thermal damage or depolarization.
5. Traditional Daily-Use Ceramics
Traditional daily-use ceramics (such as porcelain and stoneware) are usually covered with a vitreous glaze. The laser marking effect is highly dependent on the characteristics of the glaze layer. CO₂ lasers (wavelength 10.6 μm, power 20–80 W) are suitable for laser marking. W (working mode is continuous or modulated) is the preferred material for this type of material because the glaze has a good absorption rate in the far-infrared band. After laser treatment, micro-bubbles or local melting can be formed on the surface, presenting clear white or light-colored decorative marks, which are widely used for personalized customization of tableware, tea sets, art porcelain, etc.

V. Which Types of Ceramics Are Unsuitable for Laser Marking?
1. Unsintered green ceramics
2. Composite ceramics containing a high proportion of PVC or organic matter
3. High-porosity foam/honeycomb ceramics
4. Low-temperature ceramics with a thick glaze or fusible glass phase on the surface
5. High-reflectivity surface-metallized ceramics
6. Ordinary transparent ceramics
Before laser marking ceramics, it is recommended that you first conduct small-scale tests on new or unidentified ceramic materials to verify the feasibility of marking. It is essential to clearly identify the material composition, and be especially wary of ceramics containing chlorine (such as PVC), lead, or large amounts of organic binders, as these may release toxic gases under laser irradiation. During processing, ensure good ventilation and efficient fume filtration to prevent the inhalation of harmful gases.
VI. Which Ceramic Products Can Be Marked with Lasers?
✅ Industrial and Electronic Ceramics
Electronic substrates and packaging: Alumina (Al₂O₃) ceramic circuit boards, aluminum nitride (AlN) high thermal conductivity substrates, LTCC/HTCC multilayer ceramic modules, etc. To ensure product traceability, accuracy of automated assembly, and brand identification, these ceramic substrates typically require laser marking of key information such as serial numbers, QR codes, manufacturer logos, and polarity markings.
✅ Sensors and Components
In the field of sensors and components, key components such as piezoelectric ceramic (PZT) ultrasonic transducers, housings of ceramic capacitors and thermistors, and zirconia-based oxygen sensors can be processed or marked with micron-level precision using lasers during manufacturing and post-processing, while ensuring no performance damage to maintain their high sensitivity, stability, and reliability.

✅ Semiconductor and New Energy Components
In semiconductor and new energy components, key components such as silicon carbide (SiC) power module insulating substrates, ceramic insulators, and vacuum tube shells must maintain excellent high-temperature resistance and high insulation under harsh operating conditions. Therefore, their markings (such as serial numbers and manufacturer information) must employ high-temperature resistant and high-insulation laser marking technology to ensure clear readability during long-term operation without affecting device performance.
✅ Industrial Wear-Resistant Parts
In industrial wear-resistant parts laser marking applications, high-hardness components such as alumina/silicon carbide sealing rings, bearings, nozzles, and ceramic cutting tools (such as zirconia blades) require clear marking of brand, specifications, and service life indicators using high-precision laser technology. This ensures durable wear resistance and traceability under harsh operating conditions without damaging material properties.
✅ High-end Porcelain and Tableware
In high-end porcelain and tableware applications, bone china, white porcelain, and glazed stoneware can be precisely engraved with logos, patterns, or customized text on the glaze using CO₂ or fiber lasers. This achieves high-contrast, permanent marking, balancing aesthetics and personalization needs without damaging the glaze's integrity.
✅ Sanitary Ware and Building Ceramics
In the sanitary ware and building ceramics sector, laser marking technology is widely used on glazed tiles, polished tiles, and other ceramic ceramics, as well as toilets, washbasins, and other bathroom fixtures. It clearly and permanently marks brand logos, anti-counterfeiting codes, and production information, meeting both aesthetic and consistency requirements while enhancing product traceability and anti-counterfeiting capabilities.
✅ Art and Collectibles
In the art and collectibles sector, laser marking technology is used on ceramic sculptures, commemorative plates, and tea sets. It enables high-precision, delicate pattern engraving, preserving the artwork's artistic integrity while avoiding the pollution associated with traditional chemical etching, ensuring an environmentally friendly, safe, and durable marking effect.
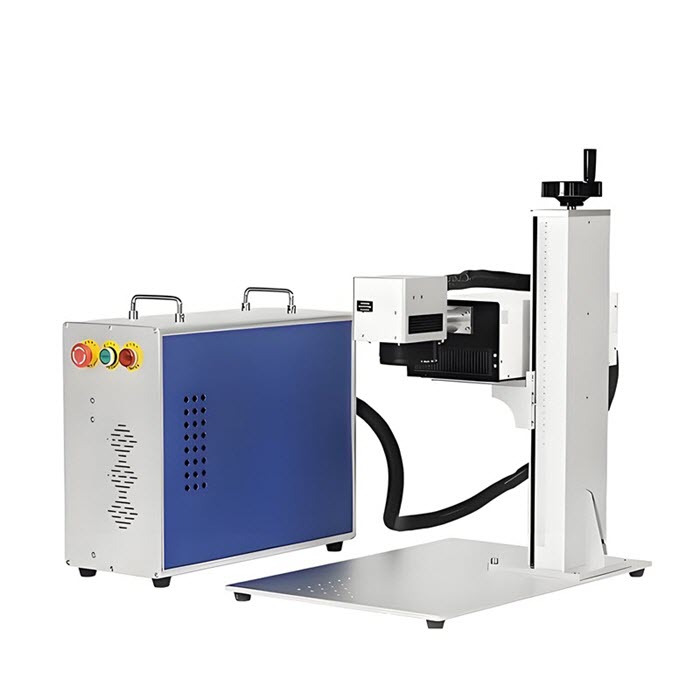
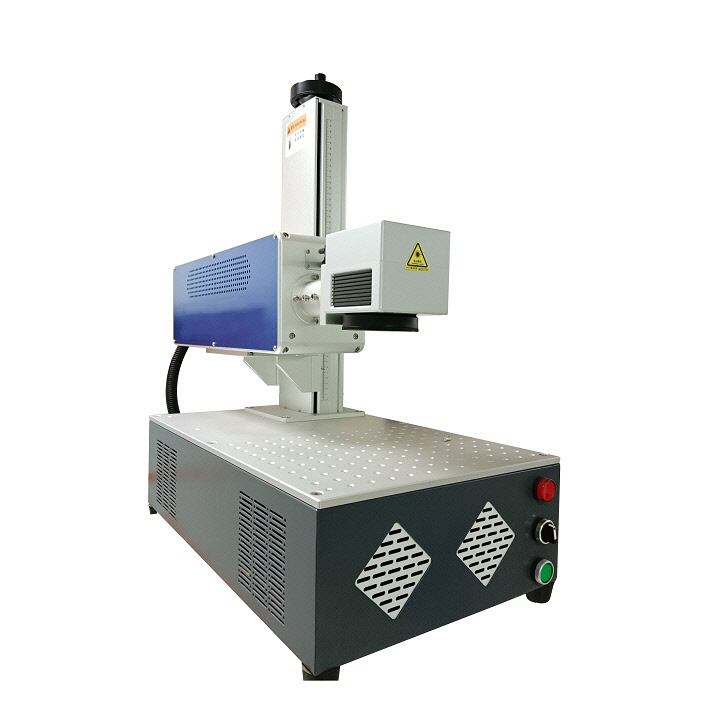
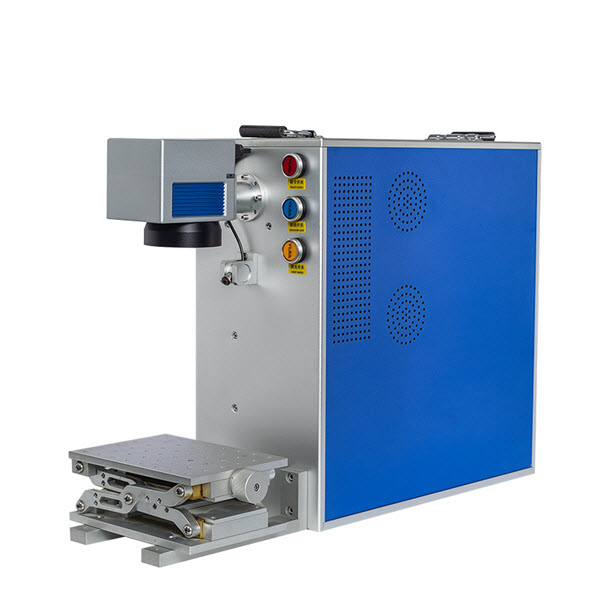
VII. How to Choose a Suitable Laser Marker for Ceramic Marking?
In laser marking applications on ceramic materials, the selection of a laser marking machine requires comprehensive consideration of factors such as ceramic type, marking effect requirements (e.g., black or white marking, precision, translucency), and production efficiency. Fiber laser marking machines and ultraviolet (UV) laser marking machines are two of the most mainstream and efficient types of equipment for marking ceramic materials.
✅ Fiber laser marking system: Suitable for dark-colored or additive-containing engineering ceramics. For the vast majority of engineering ceramics (such as alumina and zirconia), fiber laser marking machines have become the most widely used standard solution due to their high power stability, mature technology, and excellent cost-effectiveness.
✅ UV laser marking system: Suitable for high-precision, crack-free fine marking. For high-precision requirements, heat-sensitive materials, or dark-colored, transparent ceramics (such as certain glazed porcelains and special functional ceramics), UV laser marking machines are the optimal and feasible marking tool due to their cold-working characteristics, smaller heat-affected zone, and higher beam precision.
✅ CO₂ laser marking system: More suitable for traditional daily-use ceramics, glazed glass, and other non-metallic materials. When faced with ceramic materials of unknown composition or uncertain properties, do not blindly select a laser marking method or directly begin mass production. We recommend sending your ceramic samples to us for marking tests. Our technicians will experiment with different wavelengths (such as fiber optic, ultraviolet, CO₂, etc.) and parameter combinations of laser equipment on actual materials, observing key indicators such as marking effects (contrast, clarity, whether cracking or discoloration occurs), heat-affected zone, and whether harmful gases are generated. Only after fully verifying the feasibility, stability, and safety of the marking process can the most suitable laser marking equipment and process solution be scientifically selected.

VIII. What Are the Challenges and Precautions When Using Lasers for Marking on Ceramic Surfaces?
While laser marking on ceramic surfaces is a mature and widely used technology, the inherent characteristics of ceramic materials, such as high hardness, brittleness, significant differences in thermal conductivity, and complex composition, still present a series of technical challenges and operational precautions during actual processing. Only by addressing these issues appropriately can we ensure marking quality, efficiency, and safety.
1. Prone to microcracks or edge chipping (brittle cracking)
Ceramic materials are prone to microcracks or edge chipping during laser marking. High-risk materials include zirconium oxide (ZrO₂), silicon nitride (Si₃N₄), and thin-walled or edge-grown ceramic parts. This typically manifests as radial microcracks around the mark or edge debris flaking off. It is recommended to use ultraviolet lasers to reduce heat input and to preheat thick ceramic parts or control the ambient temperature and humidity.
2. High Reflectivity or Metallized Ceramic Damage
Ceramics with surface coatings of silver, aluminum, or other metals can strongly reflect fiber optic/CO₂ lasers, potentially damaging the laser marking machine's galvanometer, focusing lens, and even the laser itself. Therefore, before marking, it is essential to confirm the presence of any metal layers and install reflection protection devices or use a short-wavelength laser.
3. Dust and Fume Pollution
During the marking process, the laser ablation process generates fine ceramic dust. If not promptly removed, this dust can contaminate the optical lens, reduce marking accuracy, and affect workshop cleanliness (especially in the medical/electronics industries). Furthermore, long-term inhalation can harm human health (e.g., silicon-containing dust). Therefore, we recommend configuring a high-efficiency ventilation and filtration system (HEPA grade), regularly cleaning the galvanometer and lenses, and requiring operators to wear protective equipment.
Laser technology can be widely used for marking various ceramic materials, from industrial structural ceramics to everyday artistic ceramics, providing an efficient, precise, and environmentally friendly option for marking ceramic materials. By selecting the appropriate laser wavelength and process parameters based on the material characteristics, we can achieve permanent, environmentally friendly, and high-contrast marking, meeting multiple needs such as traceability, anti-counterfeiting, and decoration. If you would like to learn more about the details and functions of laser marking machines for ceramic materials, please feel free to contact us. If you are looking for a suitable laser marking machine to mark ceramic items, you can send us samples for free marking testing.